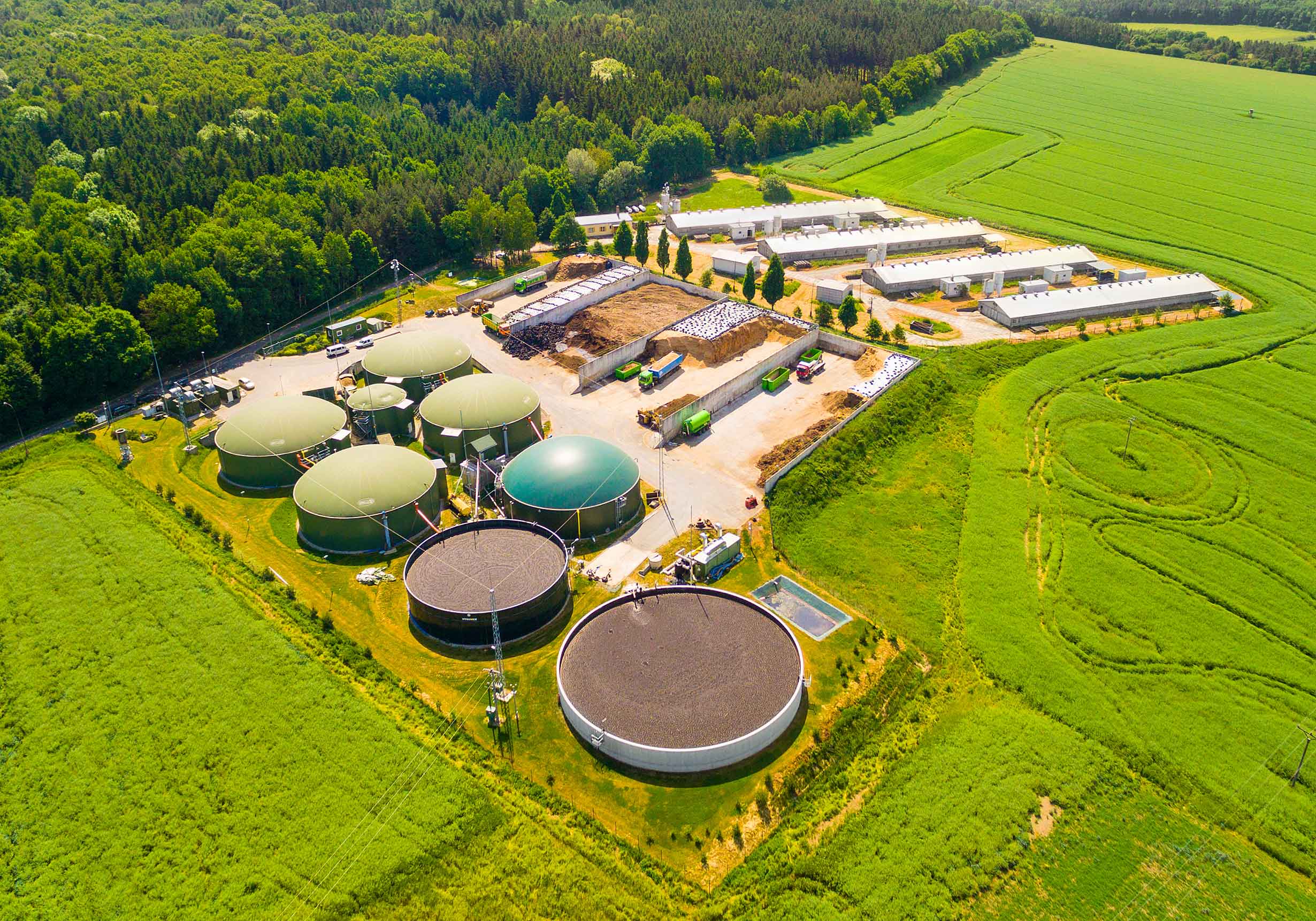

Anaerobic Digestion Technologies
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a biological process in which microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen.
The result of this process is biogas, a renewable energy source, and nutrient-rich digestate, which can be used as organic fertilizer.
The choice of AD technology depends on the type of waste, moisture content, and the economic and environmental goals of the project.
AD technologies are mainly divided into three primary categories:
1. Wet Systems
In wet AD systems, the feedstock has high moisture content (over 85–90%) and typically includes animal manure, wastewater sludge, and food waste.
Wet reactors are usually of the complete mix type (CSTR), with the material pumped and mixed to ensure optimal digestion.
Advantages:
– Suitable for very wet feedstocks
– Proven and stable technology
– Capable of handling various waste volumes
Limitations:
– High water and energy consumption for homogenization
– Large reactor volume
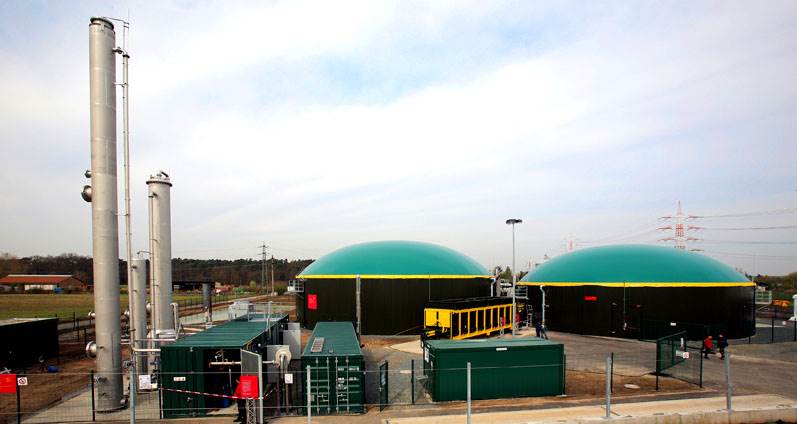

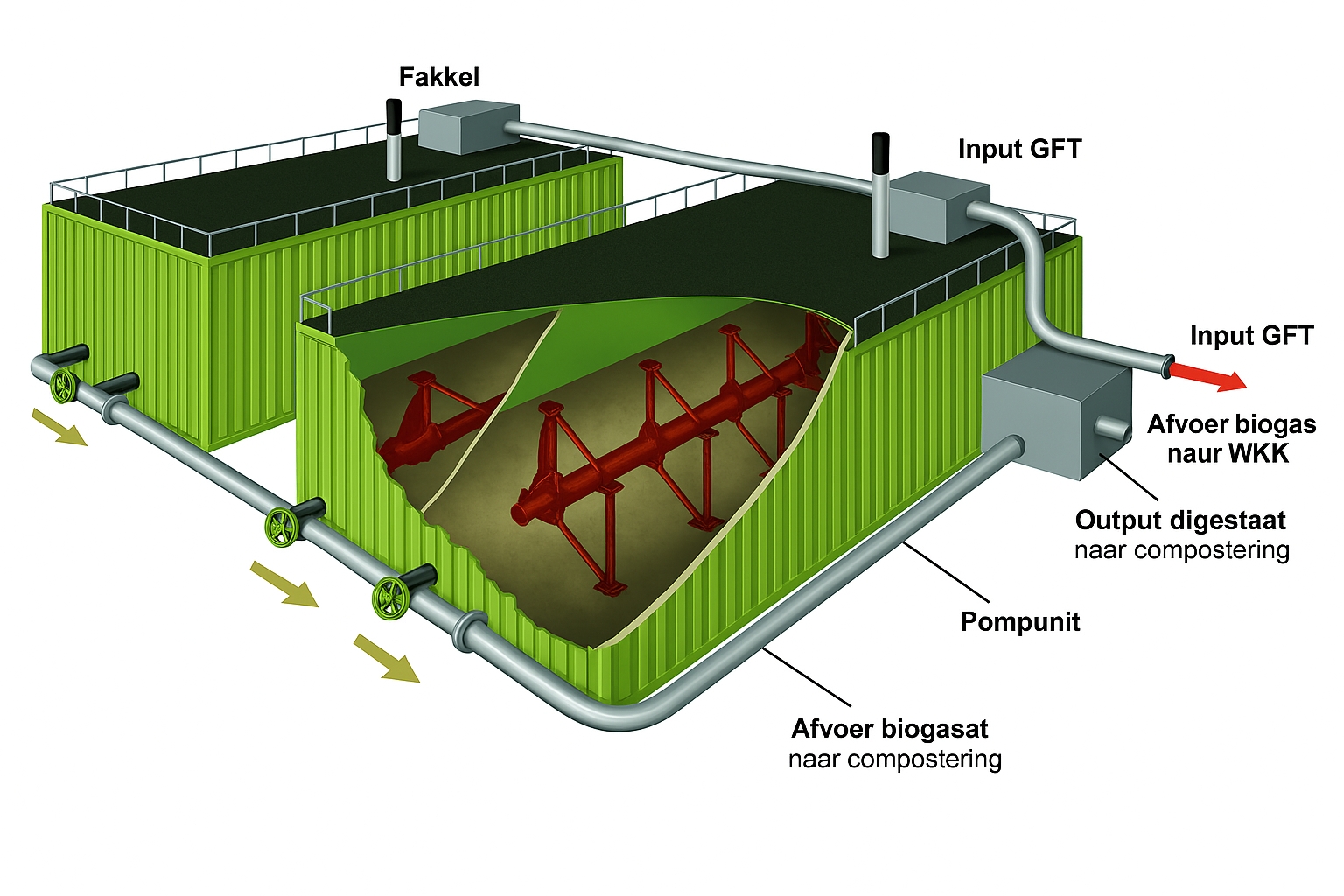
2. Continuous Dry Systems (Plug Flow)
This system is suitable for solid wastes with 20–40% moisture. The feedstock continuously enters a horizontal reactor,
moves along the path, and undergoes digestion. Continuous design allows better process control and stable methane production.
Advantages:
– High biogas yield
– Efficient use of space and energy
– Continuous and predictable operation
Limitations:
– Relatively high initial investment
– Requires advanced mechanical equipment for feeding and discharge
3. Batch Dry Systems
In batch dry systems, solid feedstock is loaded into the reactor and discharged after a specified digestion period.
This system is suitable for small to medium agricultural and industrial waste volumes and requires precise process management.
Advantages:
– High flexibility for different solid feedstocks
– Simple start-up and operation
– Suitable for small and medium capacities
Limitations:
– Lower biogas production compared to continuous systems
– Requires periodic stopping for loading and discharge
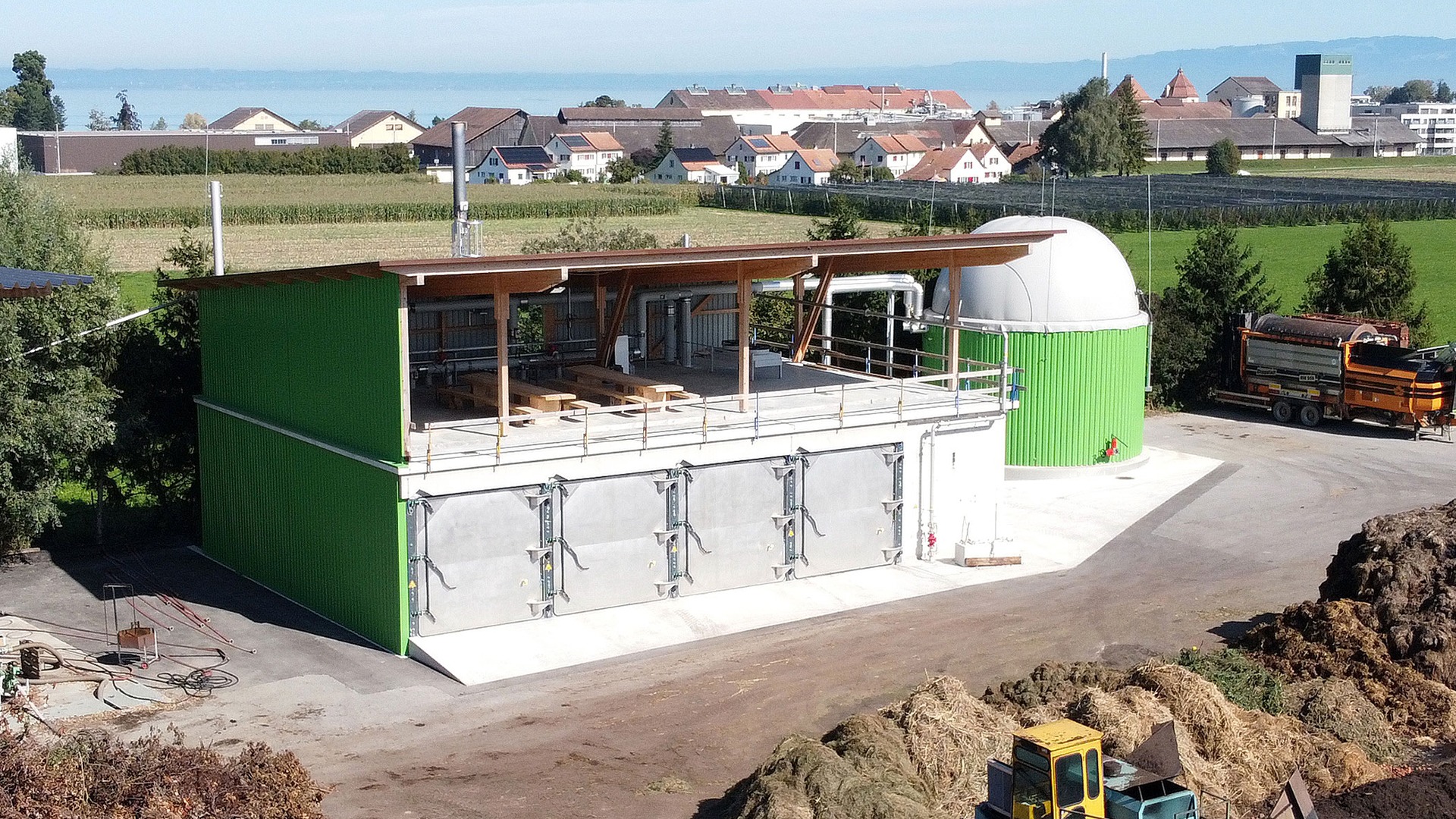

✅ Choosing the right anaerobic digestion system depends on the type of waste, project capacity, and energy and environmental goals.
The proper combination of technologies can increase energy efficiency and minimize environmental impacts.
